Lifestyle
Badshahi Mosque: A Symbol of Mughal Grandeur
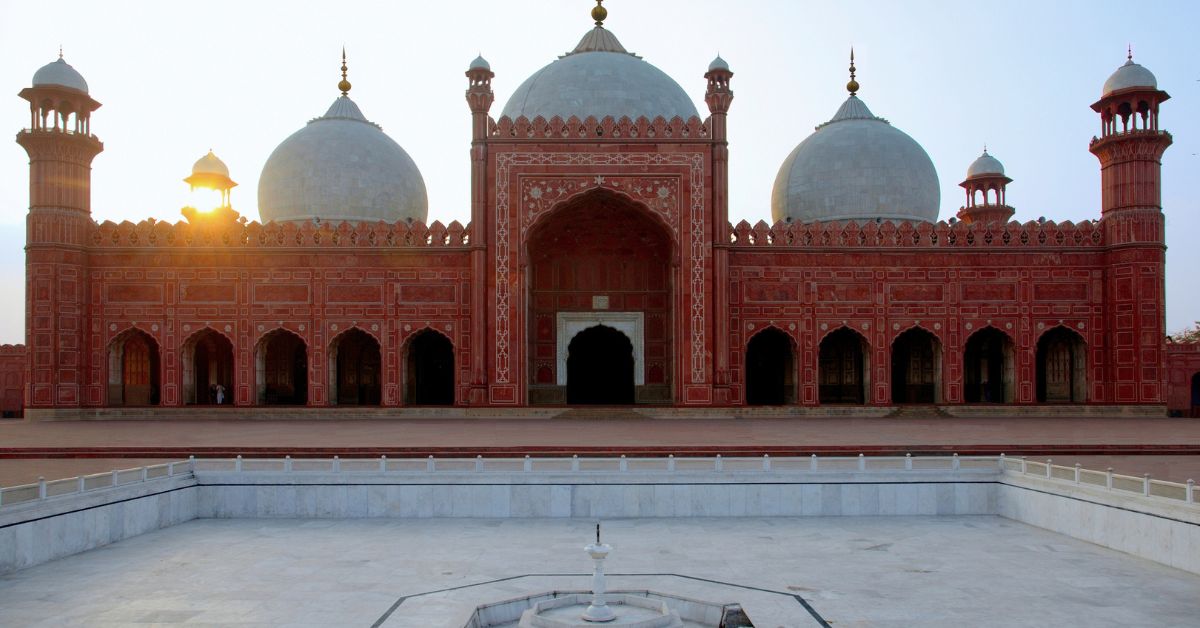

The Badshahi Mosque, located in Lahore, Pakistan, is one of the most magnificent mosques in the world and a timeless symbol of Mughal architecture. Built during the reign of the Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb Alamgir, this mosque reflects the political power, religious devotion, and artistic excellence of the Mughal Empire. Even today, it stands as a cultural, historical, and spiritual landmark admired by visitors from across the globe.
Historical Background
The Badshahi Mosque was constructed between 1671 and 1673 under the supervision of Aurangzeb’s foster brother Muzaffar Hussain (Fidai Khan Koka). It was intended to serve as the imperial mosque of the Mughal Empire and could accommodate tens of thousands of worshippers at a time. For more than 300 years, it remained the largest mosque in the world.
After the fall of the Mughal Empire, the mosque suffered neglect during the Sikh and British periods, where it was used for non-religious purposes. Restoration efforts began in the 20th century, reviving its original glory.
Architectural Features
The Badshahi Mosque is a masterpiece of Mughal architecture, combining red sandstone with white marble in elegant patterns. The mosque features a massive courtyard, four towering minarets, and three grand marble domes.
Key Architectural Highlights
- Courtyard: One of the largest mosque courtyards in the world
- Minarets: Four corner minarets, each about 196 feet high
- Domes: Three marble domes symbolizing balance and symmetry
- Calligraphy: Quranic verses inscribed in beautiful Islamic calligraphy
- Prayer Hall: Decorated with frescoes and marble inlay work
Religious and Cultural Significance
The Badshahi Mosque is not only a place of worship but also a national symbol of Pakistan. It hosts large congregations during Eid prayers, religious gatherings, and cultural events. Adjacent to the mosque lies the Lahore Fort, together forming a UNESCO World Heritage site.
Tables
Table 1: Basic Information about Badshahi Mosque
| Feature | Details |
| Location | Lahore, Pakistan |
| Built By | Emperor Aurangzeb |
| Construction Period | 1671–1673 |
| Architectural Style | Mughal |
| Primary Material | Red Sandstone & White Marble |
Table 2: Structural Dimensions
| Component | Measurement |
| Courtyard Capacity | Over 55,000 worshippers |
| Minaret Height | ~196 feet |
| Number of Domes | 3 |
| Number of Minarets | 4 |
Conclusion
The Badshahi Mosque stands as a powerful reminder of the Mughal Empire’s architectural brilliance and spiritual depth. Despite centuries of political change and neglect, the mosque has endured as a symbol of faith, unity, and cultural pride. Its grandeur, historical value, and religious importance make it one of the most treasured landmarks in Pakistan and the Islamic world.
FAQs
1. Who built the Badshahi Mosque?
The mosque was built by Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb Alamgir.
2. When was the Badshahi Mosque constructed?
It was constructed between 1671 and 1673.
3. Where is the Badshahi Mosque located?
It is located in Lahore, Pakistan, near the Lahore Fort.
4. What is the capacity of the Badshahi Mosque?
The mosque can accommodate more than 55,000 worshippers at one time.
5. Why is the Badshahi Mosque famous?
It is famous for its massive size, Mughal architecture, historical importance, and religious significance.
Lifestyle
Karakoram Range: Home of the World’s Most Dramatic Mountains

Introduction
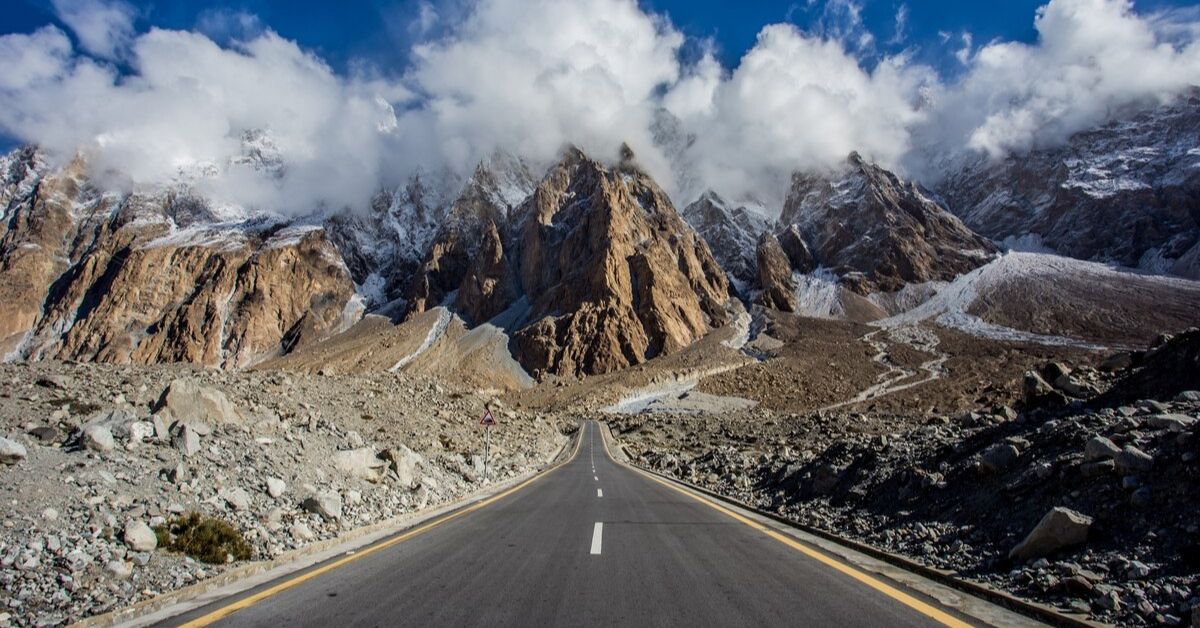
The Karakoram Range is one of the most spectacular and rugged mountain systems in the world. Stretching across parts of Pakistan, India, and China, the Karakoram is famous for its towering peaks, massive glaciers, and extreme terrain. It is home to K2, the second-highest mountain on Earth and one of the most dangerous to climb.
Unlike many other mountain ranges, the Karakoram remains wild, remote, and relatively untouched. Its harsh climate, steep relief, and geological complexity make it a place of both natural beauty and scientific importance.
Where Is the Karakoram Range Located?
The Karakoram Range lies at the crossroads of South Asia and Central Asia, spanning:
- Northern Pakistan (Gilgit-Baltistan)
- Northern India (Ladakh region)
- Western China (Xinjiang region)
It forms part of a greater high-mountain system that connects the Himalayas, Hindu Kush, and Pamir ranges.
Key Facts About the Karakoram Range
| Feature | Details |
| Continent | Asia |
| Countries | Pakistan, India, China |
| Highest Peak | K2 (8,611 meters) |
| Major Glaciers | Baltoro, Siachen, Biafo |
| Mountain Type | Fold mountains |
| Climate | Cold, arid, extreme |
| Famous Pass | Karakoram Pass |
Major Peaks of the Karakoram Range
The Karakoram contains some of the world’s tallest and most challenging mountains.
Notable Peaks
- K2 (8,611 m): Second-highest mountain in the world
- Gasherbrum I: Also known as Hidden Peak
- Broad Peak: One of the easiest 8,000m peaks (relatively)
- Gasherbrum II
- Masherbrum
Remarkably, the Karakoram has four peaks over 8,000 meters, making it one of the most concentrated regions of extreme altitude.
Glaciers of the Karakoram
The Karakoram Range contains some of the largest glaciers outside the polar regions.
Major Glaciers
- Baltoro Glacier
- Siachen Glacier (one of the longest in the world)
- Biafo Glacier
Unlike glaciers in many parts of the world, some Karakoram glaciers are stable or even advancing, a phenomenon known as the Karakoram Anomaly.
Climate and Natural Conditions
The Karakoram climate is harsh and unpredictable:
- Extremely cold winters
- Heavy snowfall at high altitudes
- Strong winds and avalanches
- Low oxygen levels
These conditions make exploration and climbing particularly dangerous.
Karakoram Range vs Himalayas
| Feature | Karakoram Range | Himalayas |
| Highest Peak | K2 (8,611 m) | Mount Everest (8,848 m) |
| Terrain | Steeper, more rugged | Broader and longer |
| Glaciers | Larger and denser | Fewer large glaciers |
| Climbing Difficulty | Extremely difficult | Comparatively accessible |
| Climate | Colder and drier | Wetter due to monsoon |
Importance of the Karakoram Range
1. Geographical Importance
The Karakoram plays a crucial role in defining regional boundaries and drainage systems.
2. Environmental Significance
Its glaciers are a major freshwater source for rivers in South Asia.
3. Strategic Importance
The region holds geopolitical significance due to its location near international borders.
4. Mountaineering and Adventure
The Karakoram attracts elite climbers seeking the ultimate challenge.
Cultural and Historical Significance
Historically, the Karakoram region was part of ancient trade routes connecting Central Asia with the Indian subcontinent. Local communities have adapted to extreme conditions and maintain unique cultures deeply connected to the mountains.
Interesting Facts About the Karakoram Range
- The name Karakoram means “Black Gravel”
- K2 has a higher fatality rate than Mount Everest
- The range has some of the steepest relief on Earth
- Many areas remain unexplored due to harsh conditions
FAQs About the Karakoram Range
1. What is the Karakoram Range famous for?
It is famous for K2, massive glaciers, and extreme mountaineering challenges.
2. Is the Karakoram part of the Himalayas?
No. It is a separate mountain range, though closely connected geographically.
3. Which is higher, Everest or K2?
Mount Everest is higher, but K2 is considered more difficult to climb.
4. Why are Karakoram glaciers not melting fast?
Due to unique climate patterns, some glaciers remain stable—known as the Karakoram Anomaly.
5. Can tourists visit the Karakoram Range?
Yes, but access is limited and often requires permits and experienced guides.
Conclusion
The Karakoram Range stands as one of the most awe-inspiring and extreme landscapes on Earth. With towering peaks like K2, vast glaciers, and unforgiving terrain, it represents the raw power of nature in its purest form. More rugged and remote than the Himalayas, the Karakoram continues to challenge scientists, climbers, and explorers alike.
As climate change and human activity increase, protecting this unique mountain system is more important than ever. The Karakoram is not just a mountain range—it is a vital natural treasure of our planet.
Lifestyle
Mount Everest: The Highest Peak on Earth

Introduction
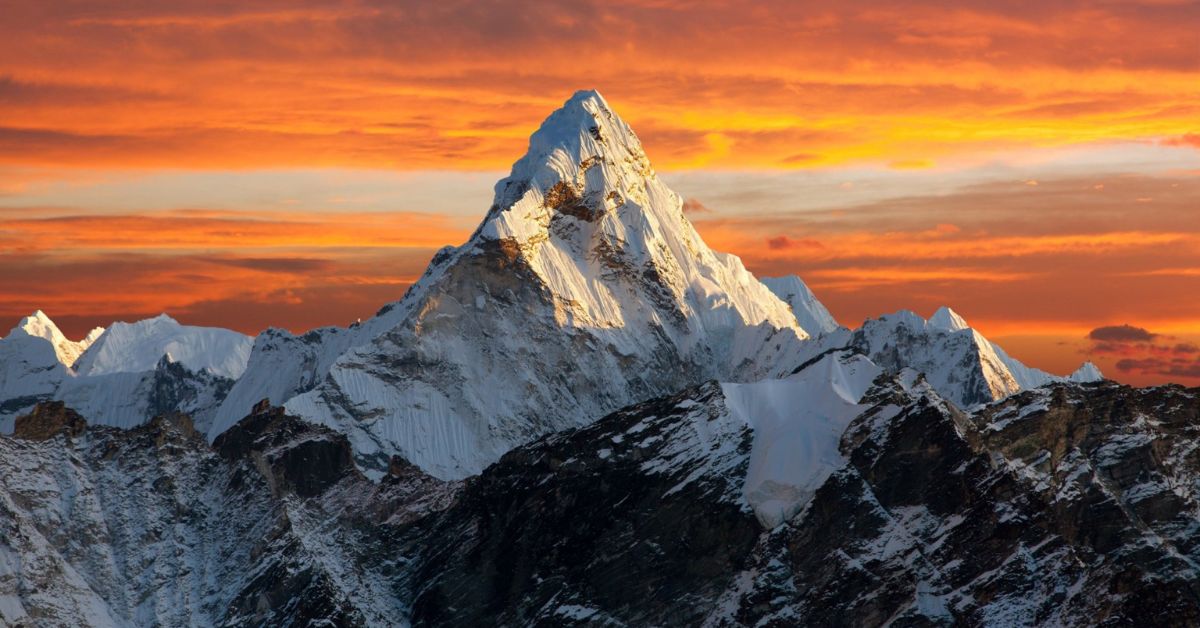
Mount Everest stands as the ultimate symbol of natural grandeur and human ambition. Rising above the Himalayas, this iconic mountain has fascinated explorers, climbers, and adventurers for centuries. Known as the highest mountain on Earth, Mount Everest represents both extreme beauty and extreme danger.
From its towering height to its deadly conditions, Everest is more than just a mountain—it is a global legend that continues to challenge the limits of human endurance.
Where Is Mount Everest Located?
Mount Everest is located in the Himalayan mountain range, on the border between Nepal and the Tibet Autonomous Region of China. It is accessible from two main routes:
- South Route: Nepal
- North Route: Tibet (China)
Key Facts About Mount Everest
| Feature | Details |
| Official Height | 8,848.86 meters (29,031.7 feet) |
| Location | Nepal–China (Tibet) border |
| Mountain Range | Himalayas |
| First Successful Ascent | 1953 |
| First Climbers | Sir Edmund Hillary & Tenzing Norgay |
| Local Names | Sagarmatha (Nepal), Chomolungma (Tibet) |
| Type | Fold mountain |
Why Is Mount Everest So Famous?
1. The Highest Point on Earth
Mount Everest is the tallest mountain above sea level, making it the ultimate goal for mountaineers worldwide.
2. Extreme Climbing Challenges
Climbers face:
- Freezing temperatures
- Low oxygen levels
- Avalanches and icefalls
- Unpredictable weather
3. Historical Significance
The first successful climb in 1953 marked a major milestone in exploration history.
Climbing Mount Everest: What It Takes
Climbing Everest is not just about strength—it requires months of preparation, experience, and mental toughness.
Requirements to Climb Everest
- High-altitude climbing experience
- Physical fitness and endurance
- Professional guides and Sherpas
- Oxygen support
- Government permits
Average Cost of Climbing Everest
| Expense Category | Estimated Cost (USD) |
| Permit Fees | $11,000 |
| Guide & Support | $30,000–$50,000 |
| Equipment & Gear | $5,000–$10,000 |
| Travel & Logistics | $5,000–$8,000 |
| Total Cost | $40,000–$75,000+ |
Environmental Impact and Conservation
Increased tourism has led to:
- Waste accumulation
- Damage to ice and ecosystems
- Overcrowding during climbing seasons
To combat this, authorities and organizations are enforcing cleanup campaigns, limiting permits, and promoting responsible climbing.
Cultural and Spiritual Importance
For local communities, Mount Everest holds deep spiritual value:
- Sagarmatha means “Forehead of the Sky” in Nepal
- Chomolungma means “Goddess Mother of the World” in Tibet
It is considered sacred and respected as a powerful natural force.
Interesting Facts About Mount Everest
- Everest grows about 4 mm taller every year due to tectonic activity
- Temperatures can drop below –60°C (–76°F)
- Over 300 people have died attempting to climb it
- Jet-stream winds can exceed 160 km/h (100 mph)
FAQs About Mount Everest
1. How tall is Mount Everest?
Mount Everest is 8,848.86 meters (29,031.7 feet) tall.
2. Can beginners climb Mount Everest?
No. Everest requires advanced mountaineering experience and physical conditioning.
3. How long does it take to climb Mount Everest?
The full expedition typically takes 6–9 weeks, including acclimatization.
4. Is Mount Everest still growing?
Yes, Everest continues to grow slightly due to tectonic plate movement.
5. Why do climbers use oxygen on Everest?
The oxygen level near the summit is extremely low, making breathing difficult and dangerous.
Conclusion
Mount Everest remains one of the most awe-inspiring natural landmarks on the planet. As the highest mountain in the world, it represents human curiosity, courage, and the desire to conquer the impossible. However, it also reminds us of nature’s power and the importance of respect, preparation, and environmental responsibility.
Whether admired from afar or climbed by the brave, Mount Everest will always stand as a symbol of Earth’s unmatched grandeur.
Lifestyle
The Future of Urban Farming in Modern Cities

Introduction
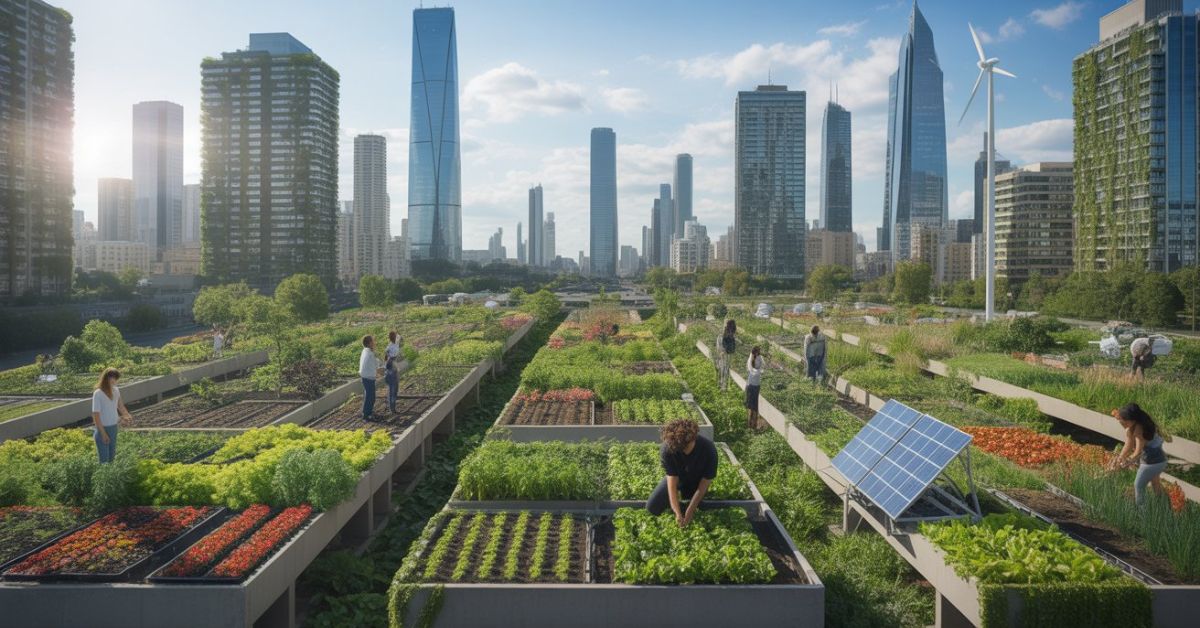
As cities expand and global populations rise, traditional farming alone can no longer meet the growing demand for fresh, sustainable food. This challenge has sparked a powerful movement: urban farming. From rooftop gardens to high-tech vertical farms, food production is moving closer to where people live.
The future of urban farming is not just about growing vegetables in cities—it’s about reshaping food systems, reducing environmental impact, and making cities more resilient. With advancements in technology and increasing focus on sustainability, urban farming is set to become a vital part of modern urban life.
What Is Urban Farming?
Urban farming, also known as urban agriculture, refers to the practice of growing, processing, and distributing food within or around cities. It includes a wide range of methods, such as:
- Rooftop gardens
- Vertical farming
- Community gardens
- Indoor hydroponic systems
- Urban greenhouses
These methods allow food to be produced in small spaces while using fewer resources than traditional agriculture.
Why Urban Farming Is the Future
1. Growing Urban Populations
By 2050, most of the world’s population will live in cities. Urban farming helps shorten food supply chains and ensures access to fresh produce.
2. Environmental Sustainability
Urban farming reduces transportation emissions, minimizes food waste, and uses water-efficient systems like hydroponics and aquaponics.
3. Food Security and Resilience
Cities that produce their own food are less vulnerable to supply chain disruptions, climate change, and global crises.
4. Technological Innovation
AI, automation, and smart sensors are making urban farming more efficient and scalable than ever before.
Types of Urban Farming Shaping the Future
| Type of Urban Farming | Description | Key Benefits |
| Vertical Farming | Crops grown in stacked layers indoors | High yield, space-efficient |
| Rooftop Farming | Gardens on building rooftops | Utilizes unused space |
| Hydroponics | Soil-free farming using nutrient water | Saves water, faster growth |
| Aquaponics | Combines fish farming with plants | Closed-loop ecosystem |
| Community Gardens | Shared neighborhood gardens | Social and food benefits |
Key Technologies Driving Urban Farming Forward
Smart Sensors and IoT
Sensors monitor temperature, humidity, nutrients, and light levels to optimize plant growth in real time.
Artificial Intelligence
AI analyzes data to predict crop yields, detect plant diseases early, and reduce resource waste.
LED Grow Lights
Energy-efficient LED lighting enables year-round indoor farming regardless of weather conditions.
Automation and Robotics
Automated systems handle planting, harvesting, and maintenance, reducing labor costs and increasing consistency.
Benefits of Urban Farming
- Fresh, local produce year-round
- Reduced carbon footprint
- Efficient water usage
- Job creation in urban areas
- Stronger community engagement
Urban farms also improve air quality and transform unused spaces into productive green zones.
Challenges Facing Urban Farming
Despite its promise, urban farming still faces several obstacles:
- High startup and energy costs
- Limited growing space
- Regulatory and zoning restrictions
- Need for technical expertise
However, as technology improves and governments support sustainable initiatives, these challenges are becoming easier to overcome.
Urban Farming and Smart Cities
Urban farming is becoming a core feature of smart city planning. Future cities are likely to integrate food production into building designs, public spaces, and infrastructure. Skyscrapers may double as farms, and residential complexes could include shared greenhouses.
This integration supports climate goals while improving quality of life for city residents.
The Future Outlook of Urban Farming
The future of urban farming is scalable, technology-driven, and community-focused. As costs decrease and awareness grows, urban agriculture will move from niche projects to mainstream food production.
Experts predict:
- Increased adoption of vertical farms
- Government incentives for urban agriculture
- Greater use of AI and renewable energy
- Expansion into developing urban regions
Urban farming will not replace traditional agriculture—but it will complement it in powerful ways.
FAQs About Urban Farming
1. Is urban farming profitable?
Yes, especially vertical and hydroponic farms that supply restaurants, grocery stores, and local markets.
2. Can urban farming feed entire cities?
While it may not fully replace rural farming, urban farming can supply a significant portion of fresh produce.
3. Is urban farming environmentally friendly?
Urban farming uses less water, reduces food miles, and lowers emissions, making it highly sustainable.
4. What crops grow best in urban farms?
Leafy greens, herbs, tomatoes, strawberries, and microgreens are most commonly grown.
5. Does urban farming require a lot of space?
No. Many systems are designed for small areas, including balconies, rooftops, and indoor rooms.
Conclusion
The future of urban farming represents a shift toward smarter, more sustainable cities. By combining innovation, technology, and environmental responsibility, urban farming offers a solution to food insecurity, climate challenges, and urban overcrowding.
As cities continue to evolve, growing food locally will no longer be an experiment—it will be a necessity. Urban farming is not just the future of food; it is the future of city living itself.
-

 Lifestyle6 months ago
Lifestyle6 months agoCristiano Ronaldo: Life, Career, and Legacy of a Football Star
-

 Lifestyle7 months ago
Lifestyle7 months agoSaiyaara Movie Overview: A Soulful Romantic Journey
-

 Lifestyle7 months ago
Lifestyle7 months agoWhat is Chainlink? Complete Guide to How It Works
-
Lifestyle7 months ago
Understanding Crypto Market Volatility: Tips for Investors
-

 Lifestyle7 months ago
Lifestyle7 months agoYellowstone National Park: Travel, Nature & Wildlife Guide
-

 Lifestyle7 months ago
Lifestyle7 months agoTrump Claims Musk ‘Off The Rails’ For Making Political Party
-

 Lifestyle7 months ago
Lifestyle7 months agoKawasaki Z650: Power, Performance, and Style Combined
-

 Lifestyle6 months ago
Lifestyle6 months agoWater in Car Engine Oil: Is It Safe to Drive?