Lifestyle
What is Chainlink? Complete Guide to How It Works
Introduction to Chainlink
Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that connects smart contracts with real-world data. In simple words, Chainlink helps blockchains talk to data outside their network. Smart contracts on blockchains are secure and automatic, but they can’t access external information on their own. This is where Chainlink comes in. It acts like a bridge between smart contracts and outside data.
For example, if a smart contract needs weather data or stock prices, Chainlink provides that data safely and accurately. It does this using Oracle’s small software programs that bring off-chain data to the blockchain. Chainlink ensures that this data is correct by using many sources to confirm the information.
Chainlink uses its own token called LINK. This token is used to pay for services within the network. Developers and businesses use LINK to reward those who provide accurate data. The project started in 2017 and has grown to become one of the top names in blockchain technology.
How Chainlink Works
To understand how Chainlink works, imagine a smart contract that needs outside data to run. Let’s say it’s a farming insurance contract. It needs weather data to decide if a payout is due. Since smart contracts can’t fetch this data directly, Chainlink steps in.
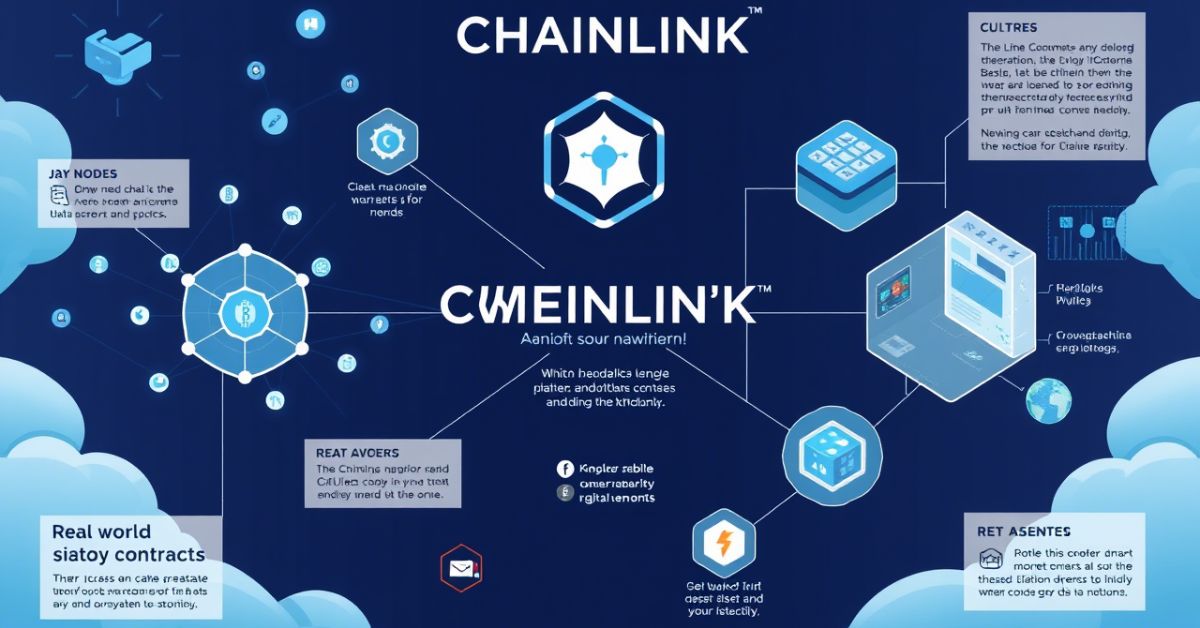
Chainlink uses oracles to fetch real-world data from APIs, sensors, or other sources. These oracles then deliver the data to the smart contract. Chainlink doesn’t rely on just one oracle. It uses many oracles to verify the data and reach a consensus. This reduces the risk of false data or system failure.
The system also uses reputation scores to rank data providers. If an oracle provides incorrect data, it may lose its ranking or stake. This helps keep the network honest. When a smart contract requests data, it pays the oracle using LINK tokens. These tokens motivate oracles to give accurate and timely information.
In short, Chainlink connects blockchains to real-world data in a safe and reliable way.
Why Chainlink is Important in Blockchain
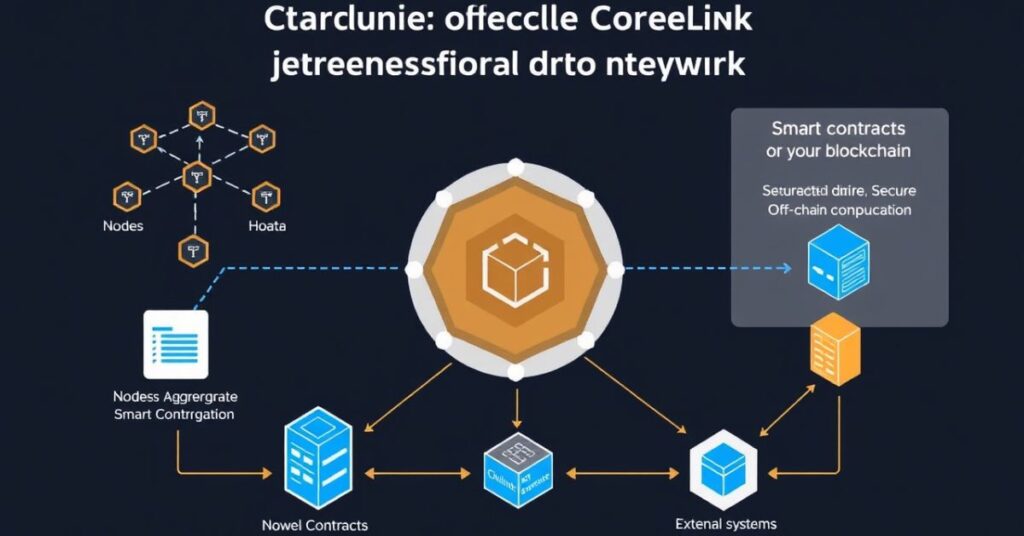
Blockchain technology is powerful but limited. One big limitation is that blockchains can’t access data from outside their network on their own. This is a serious problem because many smart contracts need real-time information.
Chainlink solves this by allowing smart contracts to connect with external data. This opens the door to many new uses. For example, Chainlink helps in areas like insurance, supply chain, finance, and gaming. A smart contract can use Chainlink to get weather updates, market prices, or even election results.
Another reason Chainlink is important is because it adds trust and security to data sharing. By using multiple sources and checking for accuracy, Chainlink ensures that smart contracts act on correct information. This prevents fraud and errors.
Chainlink also works across different blockchains. This means it can be used in Ethereum, Solana, and many other systems. It acts as a universal connector, helping apps become smarter and more useful.
Uses of Chainlink in Real-World Applications
Chainlink is not just a theory or idea. It is already being used in many real-world cases. One of the main areas is DeFi (Decentralized Finance). DeFi apps need real-time market data to run lending, trading, or insurance services. Chainlink gives them access to reliable price feeds and financial data.
In insurance, Chainlink helps with automatic payouts. For example, farmers can get insurance contracts that pay out when rainfall is below a certain level. Chainlink pulls weather data from trusted sources to check conditions and activate the contract.
In the gaming industry, Chainlink helps create fair and random results using something called VRF (Verifiable Random Function). This ensures fair play in blockchain games.
Chainlink is also helping in supply chains. It can be used to track goods, verify location data, and confirm product conditions using data from IoT devices.
Its ability to provide trusted off-chain data is what makes it so useful across many industries.
Chainlink Token (LINK): Role and Value
The native token of Chainlink is called LINK. It plays a key role in the Chainlink network. LINK is used to pay for data services and reward the oracles who bring data to smart contracts.
When someone wants to use Chainlink, they must pay the oracles in LINK. This creates demand for the token. The more Chainlink is used, the more demand there is for LINK tokens.

LINK also helps keep the network honest. Oracles can be required to stake LINK tokens before they are allowed to provide data. If they give wrong data, they lose their tokens. This system keeps everyone working fairly.
Here’s a quick look at the LINK token’s details:
| Feature | Detail |
| Token Name | Chainlink Token |
| Symbol | LINK |
| Blockchain | Ethereum (ERC-677 standard) |
| Use Case | Payment and staking for oracles |
| Max Supply | 1 Billion LINK |
The value of LINK has grown over the years because of Chainlink’s increasing use. Many people see it as a key part of the future of smart contracts.
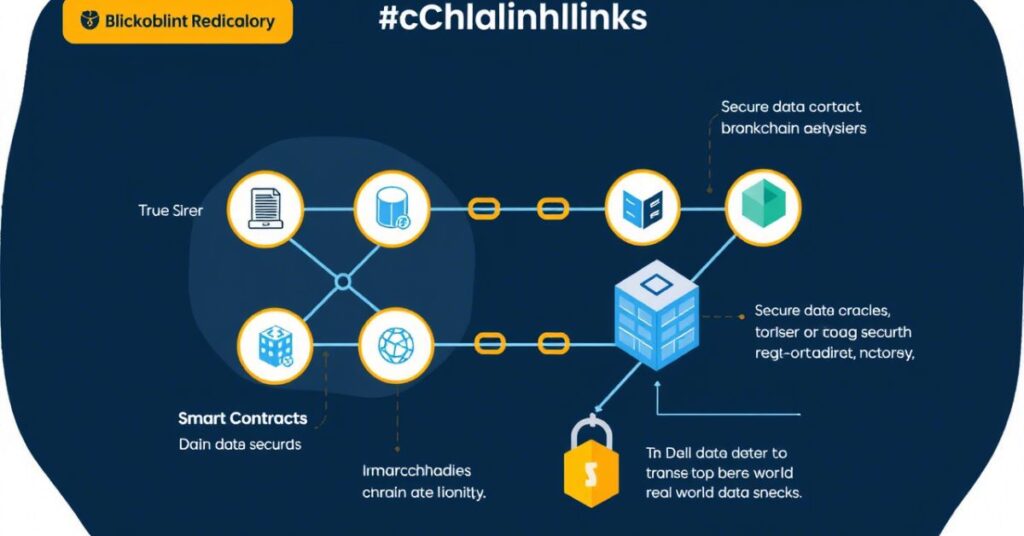
How Chainlink Ensures Data Accuracy
Chainlink uses several steps to make sure the data it provides is correct. First, it selects multiple oracles instead of just one. These oracles pull data from different sources. Chainlink then checks these answers and picks the one that most oracles agree on. This way, even if one source is wrong, it won’t affect the final result.
Chainlink also gives oracles a reputation score. This score helps decide which oracles are trusted. New oracles must earn trust over time. If an oracle sends bad data, it may lose its reputation or face a penalty.
Another feature is staking. Oracles can be required to lock up some LINK tokens before they can work. If they act dishonestly, their stake is taken away. This makes them think twice before cheating.
Chainlink also offers something called DECO and OCR (Off-Chain Reporting). These are tools to make data delivery faster and more secure. DECO helps verify private data without revealing it, and OCR reduces costs by processing data off-chain before sending it to the blockchain.
Chainlink’s Role in Web3 and Future Technology
Web3 is the next stage of the internet. It focuses on giving power back to users by using decentralized systems. Chainlink is a key part of this future. It helps Web3 apps connect to real-world data without giving up control or security.
Chainlink supports cross-chain communication through CCIP (Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol). This lets apps work across many blockchains at the same time. It makes the internet of blockchains possible.
In the future, we may see smart cities, AI tools, and automation using Chainlink to connect to real-world sensors and events. Chainlink could power apps in health, energy, and logistics by giving them trusted data.
Big companies like Google Cloud and SWIFT have worked with Chainlink. This shows that both blockchain startups and traditional businesses see value in it.
Chainlink is not just a tool; it is a core part of the growing Web3 ecosystem.
Comparison Table: Chainlink vs Other Oracle Networks
| Feature | Chainlink | Band Protocol | API3 |
| Launch Year | 2017 | 2019 | 2020 |
| Native Token | LINK | BAND | API3 |
| Decentralized | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Data Accuracy Model | Multi-oracle | Delegated Proof | First-party oracles |
| Cross-Chain Support | Strong | Medium | Low |
| Industry Adoption | High | Medium | Low |
FAQs About Chainlink
What is Chainlink used for?
Chainlink connects smart contracts with real-world data like weather, prices, and news using oracles.
Is it a cryptocurrency?
Yes, Chainlink has a token called LINK. It is used to pay for services on the Chainlink network.
Can Chainlink work with any blockchain?
Yes, Chainlink is blockchain-agnostic and works with Ethereum, Solana, and many others.
Is Chainlink safe and trustworthy?
Yes, Chainlink uses multiple oracles, reputation scores, and staking to ensure secure and accurate data.
What makes it different from others?
Chainlink focuses on decentralization, security, and real-world use. It also has strong partnerships and wide adoption.
Lifestyle
Minar-e-Pakistan: The historical building of Pakistan
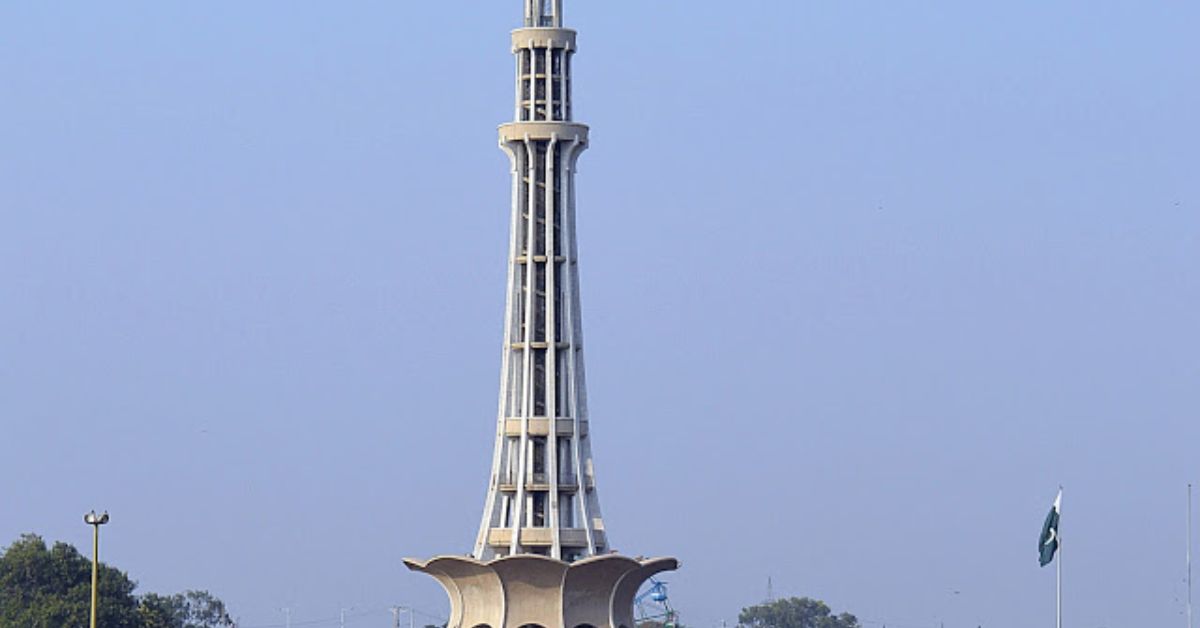

Introduction
Minar-e-Pakistan is one of the most important national monuments of Pakistan. It stands in Lahore, the cultural capital of the country, and symbolizes the struggle and sacrifices made by Muslims of the Subcontinent for a separate homeland. The monument marks the historic place where the Lahore Resolution was passed on 23rd March 1940, which later led to the creation of Pakistan in 1947.
Historical Background
On 23rd March 1940, leaders of the All-India Muslim League gathered at Minto Park (now called Greater Iqbal Park). Under the leadership of Quaid-e-Azam Muhammad Ali Jinnah, they demanded a separate state for Muslims. This demand was formally presented in the Lahore Resolution.
To commemorate this historic event, Minar-e-Pakistan was constructed. Its construction started in 1960 and was completed in 1968.
Architectural Design
Minar-e-Pakistan was designed by Nasreddin Murat-Khan, a Turkish architect. The design beautifully blends Islamic, Mughal, and modern architecture. The monument is about 70 meters high and is built with white marble, concrete, and stone.
The base of the monument has inscriptions of:
- The Lahore Resolution
- Verses from the Holy Quran
- National Anthem of Pakistan
- Speeches of Quaid-e-Azam
Key Information about Minar-e-Pakistan
| Feature | Details |
| Location | Lahore, Pakistan |
| Built Between | 1960 – 1968 |
| Height | Approximately 70 meters |
| Architect | Nasreddin Murat-Khan |
| Purpose | Commemoration of Lahore Resolution |
| Nearby Area | Greater Iqbal Park |
National Importance
Minar-e-Pakistan is not just a building; it is a symbol of freedom, unity, and determination. Every year on Pakistan Day (23rd March) and Independence Day (14th August), thousands of people visit the monument to pay tribute to the leaders of the Pakistan Movement.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. Why is Minar-e-Pakistan important?
Minar-e-Pakistan is important because it marks the place where the Lahore Resolution was passed, leading to the creation of Pakistan.
2. Who designed Minar-e-Pakistan?
It was designed by Nasreddin Murat-Khan, a Turkish architect.
3. Where is Minar-e-Pakistan located?
It is located in Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan.
4. When was Minar-e-Pakistan completed?
The construction was completed in 1968.
5. What does Minar-e-Pakistan symbolize?
It symbolizes the freedom struggle, unity, and independence of Muslims of the Subcontinent.
Conclusion
Minar-e-Pakistan holds a special place in the heart of every Pakistani. It reminds us of the sacrifices made by our leaders and forefathers for independence. The monument stands tall as a symbol of hope, unity, and national pride. Preserving and respecting such historical landmarks is our duty so future generations can learn about the glorious history of Pakistan.
Lifestyle
Burj Khalifa: The Tallest Building in the World
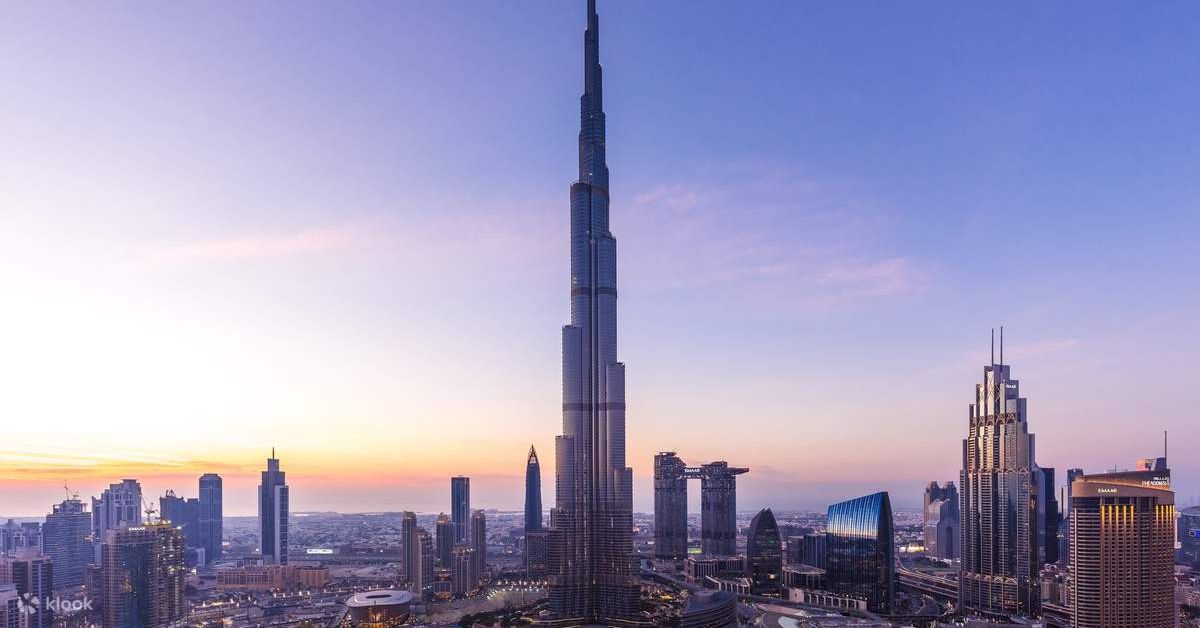

Introduction
The Burj Khalifa is an architectural masterpiece and a global symbol of innovation, located in Dubai, United Arab Emirates (UAE). Standing as the tallest building in the world, it represents human ambition, modern engineering, and economic progress. Since its inauguration in 2010, the Burj Khalifa has become one of the most iconic landmarks on Earth.
Location and Background
Burj Khalifa is situated in Downtown Dubai, surrounded by major attractions such as The Dubai Mall and Dubai Fountain. The building was developed by Emaar Properties and designed by the architectural firm Skidmore, Owings & Merrill. Its design is inspired by Islamic architecture, particularly the Hymenocallis flower.
Construction began in 2004 and was completed in 2010, showcasing cutting-edge engineering and design excellence.
Architectural Design and Structure
The tower follows a Y-shaped design, which provides stability and maximizes space for residential and hotel use. High-performance materials were used to withstand extreme temperatures, strong winds, and seismic activity.
Burj Khalifa uses advanced systems for:
- Water recycling
- Energy efficiency
- High-speed elevators
Key Facts About Burj Khalifa
| Feature | Description |
| Location | Dubai, United Arab Emirates |
| Height | 828 meters (2,717 feet) |
| Floors | 163 floors |
| Construction Period | 2004–2010 |
| Architect | Skidmore, Owings & Merrill |
| Developer | Emaar Properties |
| Primary Uses | Residential, hotel, offices, observation decks |
| World Records | Tallest building, highest observation deck, longest elevator travel |
Importance and Global Significance
The Burj Khalifa is more than just a tall building. Its significance includes:
- Boosting tourism in Dubai
- Serving as a symbol of economic growth and modernization
- Setting new standards in architectural and engineering design
It has inspired skyscraper construction projects around the world.
Observation Decks and Attractions
The Burj Khalifa features popular observation decks:
- At The Top (Levels 124 & 125)
- At The Top SKY (Level 148)
Visitors can enjoy panoramic views of Dubai, the desert, and the Persian Gulf. The tower is also famous for its LED light shows and New Year’s Eve fireworks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why is Burj Khalifa famous?
Burj Khalifa is famous for being the tallest building in the world and for its advanced engineering and design.
2. How tall is Burj Khalifa?
The building is 828 meters tall.
3. Who owns Burj Khalifa?
It is owned by Emaar Properties, a Dubai-based real estate developer.
4. Can people live in Burj Khalifa?
Yes, the building contains luxury apartments, offices, and the Armani Hotel.
5. Is Burj Khalifa open to tourists?
Yes, tourists can visit the observation decks and enjoy the views.
Conclusion
The Burj Khalifa stands as a remarkable achievement in modern architecture and engineering. Rising above the Dubai skyline, it symbolizes innovation, ambition, and progress. Beyond its record-breaking height, the tower plays a vital role in tourism, urban development, and global architectural inspiration. As a true wonder of the modern world, Burj Khalifa continues to captivate millions of visitors each year.
Lifestyle
K2 Glacier: A Vital Ice Giant of the Karakoram Range
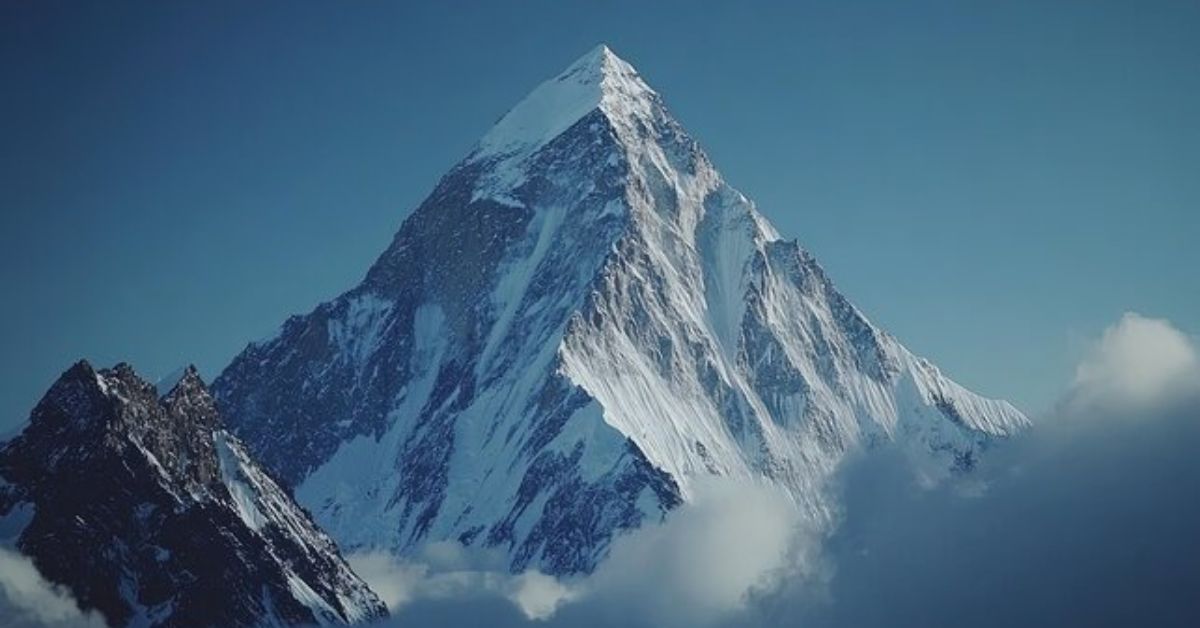

Introduction
The K2 Glacier is one of the most significant glaciers in the Karakoram Range, located near K2 (Mount Godwin-Austen), the second-highest mountain in the world. Situated primarily in Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan, this glacier plays a crucial role in regional hydrology, climate regulation, and mountain ecosystems. Known for its rugged terrain and extreme conditions, the K2 Glacier is both scientifically important and geographically striking.
Geographic Location and Formation
The K2 Glacier lies on the southern slopes of Mount K2, extending through the Karakoram mountain system. It is part of a complex network of glaciers that feed into major river systems, particularly the Indus River Basin.
Glaciers like the K2 Glacier are formed over thousands of years through the accumulation and compression of snow. Due to the high altitude and persistent cold temperatures of the Karakoram, the glacier has remained relatively stable compared to glaciers in other parts of the world.
Physical Characteristics of the K2 Glacier
| Feature | Description |
| Location | Karakoram Range, Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan |
| Associated Peak | Mount K2 (8,611 m) |
| Type | Valley glacier |
| Climate Zone | High-altitude alpine |
| Primary Water Source | Snowfall and ice accumulation |
| Drainage Basin | Indus River system |
| Terrain | Steep, rocky, heavily crevassed |
Climatic and Environmental Importance
The K2 Glacier acts as a natural freshwater reservoir, releasing meltwater during warmer months. This meltwater is essential for:
- Downstream agriculture
- Hydropower generation
- Sustaining local communities
Interestingly, glaciers in the Karakoram, including the K2 Glacier, are part of the “Karakoram Anomaly”, meaning they are more stable—or even growing—compared to many rapidly retreating glaciers worldwide.
Challenges and Risks
Despite its relative stability, the K2 Glacier faces several challenges:
- Climate change causing long-term temperature shifts
- Avalanches and icefalls due to steep gradients
- Glacial lake outburst floods (GLOFs) that threaten downstream areas
Scientific monitoring is difficult because of extreme weather and accessibility issues.
Scientific and Mountaineering Significance
The glacier is of great interest to:
- Glaciologists, studying ice dynamics and climate patterns
- Mountaineers, as it forms part of major climbing routes to K2
- Environmental researchers, monitoring climate resilience
Its harsh environment makes it one of the most dangerous yet fascinating glaciers in the world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Where is the K2 Glacier located?
The K2 Glacier is located in the Karakoram Range of Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan, near Mount K2.
2. Why is the K2 Glacier important?
It supplies meltwater to the Indus River system and plays a key role in regional water security and climate studies.
3. Is the K2 Glacier melting?
Unlike many global glaciers, it is relatively stable due to the Karakoram Anomaly, though long-term climate risks remain.
4. Can tourists visit the K2 Glacier?
Access is extremely difficult and usually limited to experienced mountaineers and scientific expeditions.
5. What makes the K2 Glacier unique?
Its high altitude, extreme terrain, and unusual stability in a warming world make it scientifically unique.
Conclusion
The K2 Glacier is a vital component of the Karakoram ecosystem and a crucial freshwater source for millions of people downstream. While it remains relatively stable compared to many glaciers worldwide, ongoing climate change and environmental pressures pose future risks. Continued research, monitoring, and conservation efforts are essential to understand and protect this remarkable glacier for generations to come.
-

 Lifestyle6 months ago
Lifestyle6 months agoCristiano Ronaldo: Life, Career, and Legacy of a Football Star
-

 Lifestyle6 months ago
Lifestyle6 months agoSaiyaara Movie Overview: A Soulful Romantic Journey
-
Lifestyle7 months ago
Understanding Crypto Market Volatility: Tips for Investors
-

 Lifestyle6 months ago
Lifestyle6 months agoYellowstone National Park: Travel, Nature & Wildlife Guide
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoWater in Car Engine Oil: Is It Safe to Drive?
-

 Lifestyle7 months ago
Lifestyle7 months agoTrump Claims Musk ‘Off The Rails’ For Making Political Party
-

 Lifestyle6 months ago
Lifestyle6 months agoKawasaki Z650: Power, Performance, and Style Combined
-
Lifestyle6 months ago
Ethereum Explained Simply: Use, Benefits & Future